PROJECT DESCRIPTION
Salt diapirs are pillar- or wall-shaped structures of viscous evaporites, which buoyantly rise adjacent to subsiding sedimentary layers. The top part of these structures is usually formed by polygenetic mélange of less soluble rocks – ‘caprock’, formed by gypsum dominated dissolution breccia, as the diapirs are dissolved by unsaturated fluids. In this project, we want to investigate the structure, composition and mechanical properties of the caprock by combined structural mapping in Iran (Zagros Fold and Thrust Belt) and analog modeling. In the analog models, we try to reproduce the deformation patterns in the caprock on top of rising salt diapirs, which are affected by tectonic shortening. Salt is represented by high viscosity silicone putty and sedimentary host rocks are formed by granular materials (sand and cenosphere mixtures). As a caprock material, we use various mixtures of granulates and powders in order to vary its physical properties, such as density and frictional strength.
This analog modelling study is part of the bi-lateral project ‘Influence of caprock on the growth dynamics of salt diapirs in Iran’ funded by GAČR and DFG (No. 20-18647J) in cooperation with the Department of Earth and Environmental Sciences of the Ludwig-Maximilians-University Munich. In this integrative project, we also perform geological and geophysical field studies at the salt diapir outcrops in Southern Iran as well as numerical modelling dealing with deformation patterns in the caprock during reactivation of the salt diapir growth. With this approach, results of the analog modelling are improved in the spatial and temporal resolution and compared with results of these complementary methods.
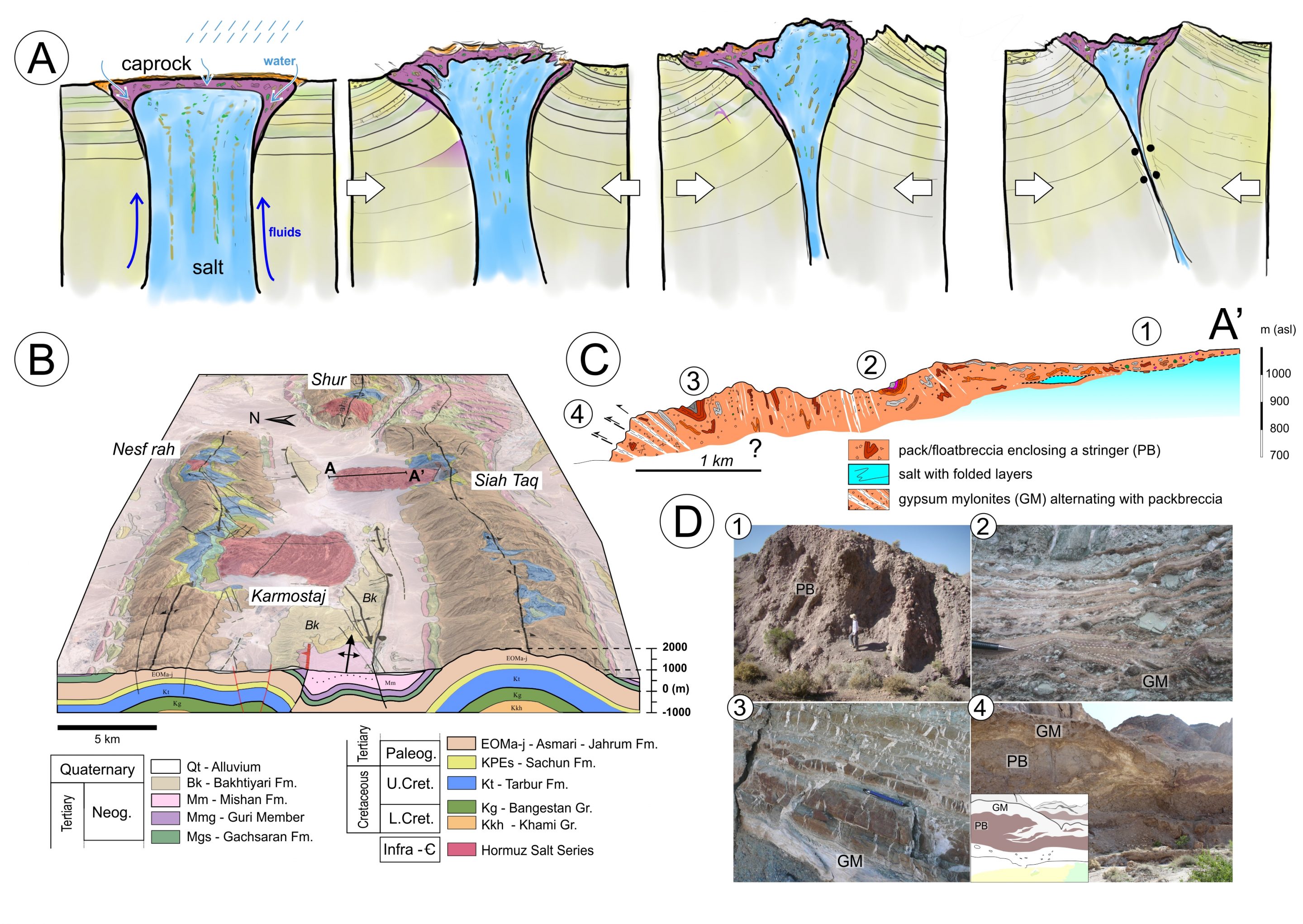
Deformation of caprock on top of salt diapir in the Zagros mountains (Southern Iran). (a) Conceptual scheme illustrating the gradual reactivation of a diapir with overlying caprock, (b) a block diagram with salt diapirs in Southern Iran with an indicated structural profile, (c) photographs illustrating deformation of the caprock (1 – packbreccia, 2 – gypsum mylonites, 3 – gypsum veins crosscutting a carbonate/sandstone stringer, 4 – gypsum mylonites alternating with packbreccia); Závada et al., (2021).
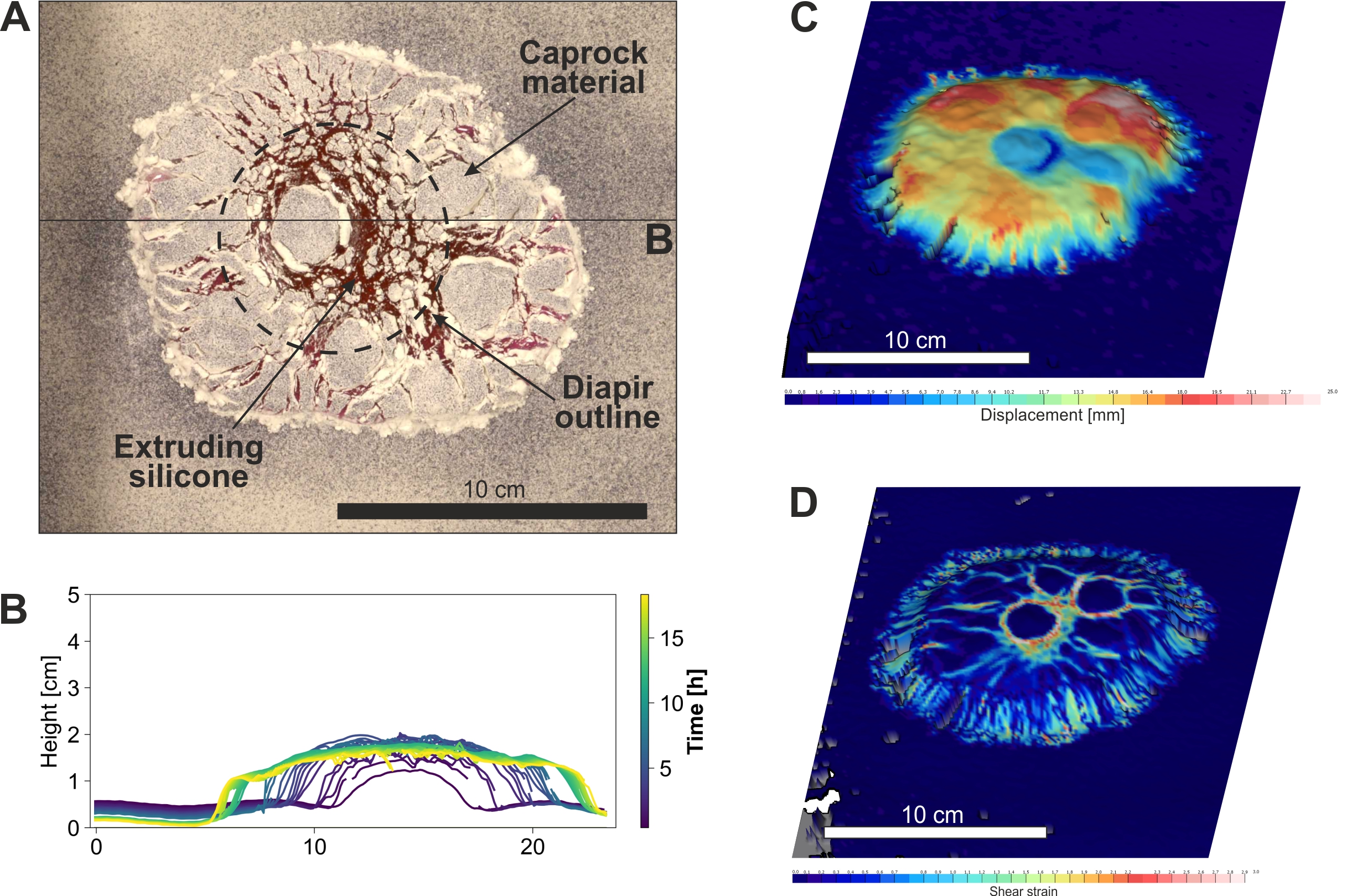
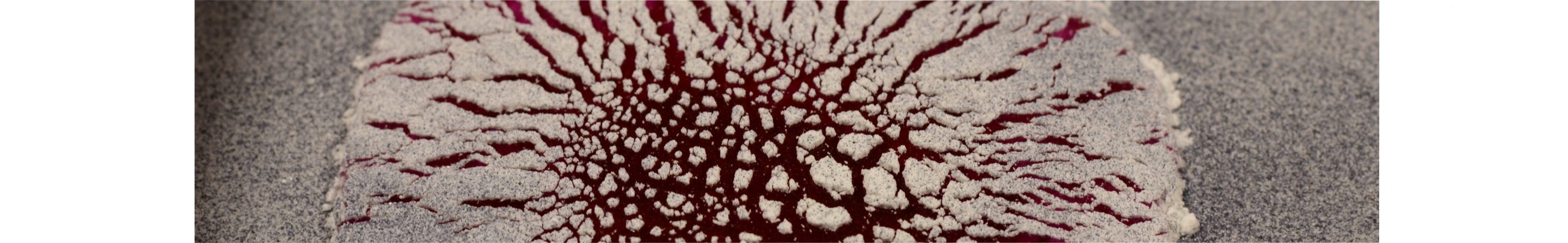
Analog experiment of a salt extrusion with overlying caprock layer. (A) Top view photo of extruded viscous silicone (red) and dismembered, cohesive caprock material (white). (B) Evolution of the surface topography extracted along a horizontal profile. (C) 3D displacement patterns. (D) 3D patterns of the shear strain illustrating the fracture pattern in the caprock.
Publications
Papers
- Závada, P., Bruthans, J., Adineh, S., Warsitzka, M., & Zare, M. (2021). Composition and deformation patterns of the caprock on salt extrusions in southern Iran–Field study on the Karmostaj and Siah Taq diapirs. Journal of Structural Geology, 151, 104422, doi: 10.1016/j.jsg.2021.104422
Conference contributions
- Závada, P., Bruthans, J., Adineh, S., Warsitzka, M., & Zare, M. (2021, April). Intense deformation of the caprock on salt extrusions in the Iranian Zagros Mountains-Insights from geological mapping and analogue modeling. In EGU General Assembly Conference Abstracts (pp. EGU21-14873).
Period
2020-2022
Researcher
Michael Warsitzka
Barbora Píšová
Collaborators & Visitors
- Prof. Anke Fredrich (Ludwig-Maximilians-University Munich)
- Doc. RNDr. Jiří Bruthans (Charles University Prague)
- Michał Słotwiński (University of Wroclaw)
Funding
- GAČR No. 20-18647J